2.0 System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
2.1 Introduction To SDLC
Candidates should be able to:
(a) describe systems development methodologies: waterfall model, rapid application development model and spiral model;
(b) describe the phases in SDLC: planning, analysis, design, implementation and maintenance with reference to waterfall model.
这里先把SDLC的5个Phase讲完,不包括几种model.....不然真的很长,SDLC是stpm里常出的热门题目,每个phase都要理解清楚,也是最长的一个bab。*代表额外知识。
System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
-A conceptual model which includes policies and procedures for developing or altering systems throughout their life cycles.
-Used by analysts to develop an information system.
-A systematic approach which explicitly breaks down the work into phases that are required to implement either new or modified Information System.
>把系统发展分成几个周期(phase) ,通常是5个
>简单来说,分成5个phase去设计发展一个软件、系统等
#stpm里不把testing phase当成其中一个SDLC------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2.2 Planning Phase
Candidates should be able to:
(a) state the purpose of the planning phase;
(b) describe and perform the activities in the planning phase: initial evaluation and feasibility study;
(c) produce the deliverables of the planning phase: feasibility report, problem statement, project objective, project scope and project schedule.
Planning Phase
-Purposes:
~To find out the scope of the problem and determine solutions
~To decide exactly what you want to do and the problems you’re trying to solve
-Activities:
~Initial evaluation
- Investigates the current system to define problems, the objectives and the resources such as personnel and costs.
~Feasibility Study
-Suggestions:
~Develop a new system
~Improve the current system
~Leave the system as it is.
-Deliverables:
- Feasibility report
- Problem statement
- Project objective
- Project scope
- Project schedule
>简单的说就是会去研究现有的系统需要改进吗,还符合顾客要求吗,如果需要就进行下一个phase,不需要就保持不动。
Feasibility Study
-Designed to reveal whether a project/plan is feasible.
-Conducted in order to objectively uncover the strengths and weaknesses of a proposed project or an existing business.
-To decide whether the current system still meets the user's needs.
-To determine whether the proposed system is suitable for all the organisation sources.
-Types of feasibility study:
1.Economic Feasibility
- Involves a cost/ benefits analysis of the project, helping organizations determine the viability, cost, and benefits associated with a project before financial resources are allocated.
- It also serves as an independent project assessment and enhances project credibility—helping decision-makers determine the positive economic benefits to the organization that the proposed project will provide.
- 调查cost和一些可能带来的好处
2.Technical Feasibility
- To determine whether the current resources can support the future expansion or able to communicate with other systems.
- Focuses on the technical resources available to the organization.
- It helps organizations determine whether the technical resources meet capacity and whether the technical team is capable of converting the ideas into working systems.
- Technical feasibility also involves the evaluation of the hardware, software, and other technical requirements of the proposed system.
- 调查现有的技术能支持系统发展吗,公司有相关的技术和科技吗。
3.Operational Feasibility
- To analyze and determine whether—and how well—the organization’s needs can be met by completing the project.
- Examine how a project plan satisfies the requirements identified in the requirements analysis phase of system development.
- To determine whether the system is operating effectively once it is developed and implemented.
4.Legal Feasibility
- Investigates whether any aspect of the proposed project conflicts with legal requirements like zoning laws, data protection acts or social media laws.
- Exp: An organization wants to construct a new office building in a specific location. A feasibility study might reveal the organization’s ideal location isn’t zoned for that type of business. That organization has just saved considerable time and effort by learning that their project was not feasible right from the beginning.
- 调查要发展的系统有没有违反法律等
5.Social Feasibility
- To determine whether the proposed system can be accepted by the society.
6.Scheduling Feasibility
- Estimates how much time the project will take to complete.
- Ensure the project is completed within the given time schedule.
- 调查能在规定时间完成吗
*Importance of Feasibility Study
-Improves project teams’ focus
-Identifies new opportunities
-Provides valuable information for a “go/no-go” decision
-Narrows the business alternatives
-Identifies a valid reason to undertake the project
-Enhances the success rate by evaluating multiple parameters
-Aids decision-making on the project
-Identifies reasons not to proceed
#搬运自https://www.google.com/amp/s/www.simplilearn.com/feasibility-study-article/amp
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2.3 Analysis Phase
Candidates should be able to:
(a) state the purpose of the analysis phase;
(b) describe the activities in the analysis phase: determination of users’ requirements and structuring of system requirements;
(c) state the methods of determining users’ requirements: interview, survey, observations, and review of procedures and documents;
(d) apply suitable methods of determining users’ requirements;
(e) describe structuring of system requirements: process modeling, logical modeling and conceptual data modeling;
(f) use data flow diagrams to model the processes;
(g) use logical model representations: decision tree and decision table;
(h) use entity-relationship (E-R) diagrams to model conceptual data;
(i) produce the deliverables of the analysis phase: users’ requirements specifications, process model, decision tree or decision table and data model.
Analysis Phase
-Defines the requirements of the system, independent of how these requirements will be accomplished.
-Defines the problem that the customer is trying to solve.
>分析顾客需求,一些问题
-Activities:
~Determination of users' requirement
~Structuring of system requirement
-Deliverable:
- Users' requirements specifications
- Process model decision tree
- Process model decision table
- Data model
Determination of Users' Requirement
-Data collecting techniques:
1.Interview
- A structured conversation where one participant asks questions, and the other provides answers.
- System analyst will be the interviewer while system user is the interviewee.
- Advantages:
-Effective way of communicating and obtaining information.
-Allow open-end questions.
-Flexible, questions are not fixed. - Disadvantages:
-Time consuming
-Costly
-Limited number of questions and people can be covered.
2.Questionnaires/Survey
- Allow an analyst to collect information from many people in relatively short amount of time.
- Documents that contained a set of standard questions that can be sent to many individuals for collecting information about the system.
- When using questionnaires, the questions should be focused and organized by a feature or project objective.
- Questionnaires should not be too long, to ensure that users will complete them.
- Advantages:
-Able to collect data from a large group of people
-Identity of respondents will not be known which encourage them to provide real facts. - Disadvantages:
-Number of replies is not guaranteed.
-Takes a long time to get a reply.
-Inflexible.
3.Observations
- A process of watching someone or something.
- System analyst can observe the user and how their surroundings affect their interaction with the system
- Advantages:
-Analyst can understand system better.
-Able to see how the users operate the current system.
-Inexpensive. - Disadvantages:
-Direct observation may distract staff and causes poor performances.
-Need multiple sessions to verify that facts collected were constant, rather than isolated incidents. -Users may not provide an accurate depiction of their everyday tasks and respond differently.
-Some users may become nervous, and not perform as they normally would. Other users may try and perform better or work harder when they know they are being observed. Such observations can inhibit the analyst to decipher what the true requirements actually should be.
4. Review of procedure and documents
- Help the analyst understand the business, or system, and its current situation.
- Provide the analyst the titles and names of stakeholders who are involved with the system.
- Help the analyst formulate questions for interviews or questionnaires to ask of stakeholders, in order to gain additional requirements
- Advantages:
-Discover more details about the current system
-Economical
*Joint Application Design (JAD)
-A structured process in which users, managers, and analysts work together for several days in a series of intensive meetings to specify or review the system requirements.
-A process that accelerates the design of information technology solutions.
-Person involved:
~Project Leader
~Session Leader
~Scribe/Modeler
~Participants (Managers, Users)
~Observer
-Advantages:
Consolidation of months of work into a structured workshop
Clarifies specification requirements in an environment of consensus
Identifies open issues and parties responsible for their resolution
Ties together the steps of the design process in a concise document
Increases user satisfaction by directly involving users in the design process
Builds commitment through the use of the executive sponsor
Builds a sense of belonging and helps create a cohesive team through the physical and social setting#部分来源https://www.umsl.edu/~sauterv/analysis/F2015/Requirement%20Gathering%20Methods.html.htm
Structuring of System Requirement
1.Process modeling
- Organize and utilize the information gathered during requirements determination into a meaningful representation of the IS that exists.
- Graphically represent the functions or processes that capture, manipulate, store and distribute data between a system and its environment and among system components
- Exp: Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
- Able to know how data flows through an information system (i.e. between external entities and the processes and data stores within a system), the relationship among data flows, and how data is stored at specific locations. the processes that change or transform data.
2.Logical modeling
- Model the processing logic and the timing of the events.
- Involves representing internal structure and functionality of processes depicted on a DFD.
- Processes must be clearly described before translating them into a programming language.
- To show when processes on a DFD occur.
- Logic modeling will be generic without taking syntax of a particular programming language
3.Conceptual data modeling
- Representation of organizational data.
- An organized view of database concepts and their relationships.
- To show rules about the meaning and interrelationships among data and to create accurate E-R diagrams
- Entity-Relationship (E-R) diagrams are commonly used to show how data are organized.
- Consistency must be maintained between process flow, decision logic, and data modeling description.
- Methods such as interviews, questionnaires, and JAD are used to collect information
#https://slideplayer.com/slide/12310271/
更详细的请到链接里看或者自己找别的网站,这里不多解释,后面design phase还会有类似的出现。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2.4 Design Phase
Candidates should be able to:
(a) state the purpose of the design phase;
(b) describe and perform the activities in the design phase: logical data design, physical data design and program structure design;
(c) produce the deliverables of the design phase: logical data design, user interfaces, form design, report design and program structures using structure charts.
Design Phase
-Describe the necessary specifications, features and operations that will satisfy the functional requirements of the proposed system which will be in place.
-This is the step for end-users to discuss and determine their specific business information needs for the proposed system.
-Consider the essential components (hardware and/or software) structure (networking capabilities), processing, and procedures for the system to accomplish its objectives.
-Activities:
- Logical Data Design
-To define the structure of data elements and to set relationships between them.
-Adds further information to the conceptual data model elements.
-To provide a foundation to form the base for the Physical model.
- Physical Data Design
-Describes a database-specific implementation of the data model.
-It offers database abstraction and helps generate the schema.
-Helps in visualizing database structure by replicating database column keys, constraints, indexes, triggers, and other RDBMS features.
- Program Structure Design
-A conceptualization of the problem into several well-organized elements of solution.
-A systematic methodology to determine design specification of program.
-It is basically concerned with the solution design.
-Gives a better understanding of how the problem is being solved.
-Deliverable:
- Logical data design
- User interfaces
- Form design
- Report design
- Program structures using structure charts.
*Structure Chart
-A chart that shows the breakdown of a system to its lowest manageable levels.
-Represent hierarchical structure of modules.
-Structure Analysis Tools:
- Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
- Data Dictionary
- Structured English
- Decision Tree
- Decision Table
#https://www.guru99.com/data-modelling-conceptual-logical.html#5
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2.5 Implementation Phase
Candidates should be able to:
(a) state the purpose of the implementation phase;
(b) describe and perform the activities in the implementation phase: coding, testing, installation, evaluation, documentation, training and support;
(c) explain the types of testing: manual (inspections, walkthroughs and desk checking) and automated (syntax checking, unit testing, integration test and system test) and user acceptance testing (alpha and beta);
(d) produce the deliverables of the implementation phase: test report, installed system (direct, parallel, pilot and phased) and documentation (system and user);
(e) explain user training and support: (design and content) and (method and delivery).
Implementation Phase
-Involves the actual installation of the newly-developed system.
-This step puts the project into production by moving the data and components from the old system and placing them in the new system via different methods.
-To deploy and enable operations of the new information system in the production environment.
-Activities:
- Coding
-Developers start build the entire system by writing code using the chosen programming language.
-Tasks are divided into units or modules and assigned to the various developers. -Developer needs to follow certain predefined coding guidelines.
-They also need to use programming tools like compiler, interpreters, debugger to generate and implement the code.
- Testing
-To detect errors that still appear in the system.
-Test the functionality of the entire system.
-To verify that the entire application works according to the customer requirement.
-This process continues until the software is bug-free, stable, and working according to the business needs of that system.
- Installation
-Install a copy of software so user can use it.
-The final software is released and checked for deployment issues if any.
-Replace the current system with new system.
- Evaluation
-Measures how well the original ambitions of the new system have been achieved.
- Documentation
-Represents documents that describe the system itself and its parts.
- Training and Support
-Teaching, or developing in oneself or others, any skills and knowledge or fitness that relate to specific useful competencies.
-Training helps users adapt to changes in their roles while support helps end-users prevent issues from the get-go.
-Support enables the evolution of the platform to better meet the needs of the organization from spotting new enhancements to finding bugs that could hamper the workday.
-Deliverable:
- Test report,
- Installed system (direct, parallel, pilot and phased)
- Documentation (system and user)
Types of Testing
- Manual Testing
-Process of manually testing software for defects.
-Execute text cases manually by a tester without using any automated tools.
➤Inspections
-An organized examination or formal evaluation exercise.
-Refers to peer review of any work product by trained individuals who look for defects using a well-defined process.
-Formal form of reviews and strategy adopted during the static testing phase.
#http://tryqa.com/what-is-inspection-in-software-testing/
➤Walkthrough
-Method of conducting informal group or individual review.
-To review documents with peers, managers, and fellow team members who are guided by the author of the document to gather feedback and reach a consensus.
-Can be pre-planned or organized based on the needs.
>比较不正式的测
#http://tryqa.com/what-is-walkthrough-in-software-testing/
➤Desk Checking
-The process of manually reviewing the source code of a program.
-It involves reading through the functions within the code and manually testing them, often with multiple input values
- Automated Testing
➤Unit Testing
-A type of software testing where individual units or components of the software are tested.
-To validate that each unit of the software code performs as expected.
-Unit Testing is done during the development (coding phase) of an application by the developers. -Unit Tests isolate a section of code and verify its correctness.
-A unit may be an individual function, method, procedure, module, or object.
>单个测
#https://www.guru99.com/unit-testing-guide.html
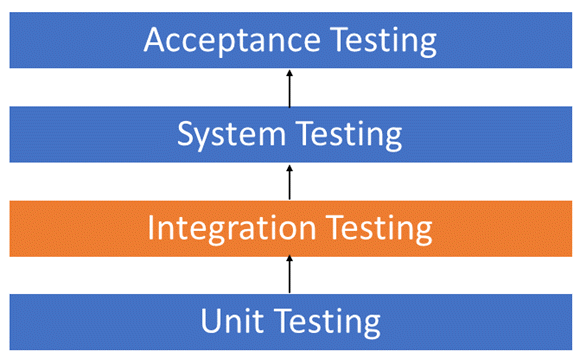
➤Integration Testing
-Software modules are integrated logically and tested as a group.
-To expose defects in the interaction between these software modules when they are integrated.
>合起来测
#https://www.guru99.com/integration-testing.html
➤System Testing
-A level of testing that validates the complete and fully integrated software product.
-To evaluate the end-to-end system specifications.
#https://www.guru99.com/system-testing.html
➤Syntax Checking
-A program to check natural language syntax.
-Check syntax errors in each statement, according to the data set type.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
-A type of testing performed by the end-user or the client to verify/accept the software system before moving the software application to the production environment.
-UAT is done in the final phase of testing after functional, integration and system testing is done.➤Alpha Testing
-A type of software testing performed to identify bugs before releasing the product to real users or to the public.
-A form of internal acceptance testing performed mainly by the in-house software quality assurance and testing teams.
-To test the overall system to see whether it meets the design requirements.
-Uses simulated data that is prepared by the tester.
>内部人员自己测
➤Beta Testing
-Performed by real users of the software application in a real environment.
-To test the capabilities of the system in the user environment.
-Uses actual data.
>给真实用户测试
#https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-alpha-and-beta-testing/
Installation Methods
- Direct Replacement/Conversion
-A hardware or software migration method that involves rolling out the new system to a small group of users for testing and evaluation.
-The old system stops getting used one day and new system starts being used the next.
>直接把旧的系统停用,换上新系统
- Parallel Running/Replacement
-Old system and new system are run alongside each other for period of time.
-When the new system is used at the same time as the old system.
>旧和新的系统同时一起用
- Pilot Running/Approach
-When a small group of users within an organization uses a new system prior to wider use.
-Can test the system works properly without having to massively restructure the company.
>先让一小部分用新系统,再慢慢扩大更新范围
- Phase Replacement
-When small parts of the new system gradually replace small parts of the old system.
-New system is implemented one part at a time in phases.
>先更新系统一小部分,之后测试没有问题再更新其他部分
Types of Documentation
- System Documentation
-Records detailed information about a system’s design specifications, its internal workings, and its functionality.
-Much more technical.
-Includes things like source code, testing documentation and API documentation(programmers’ documentation or instructions).
-It describes the requirements and capabilities of the software and informs the reader about what the software can and can’t do – in other words, its functionality.
- User Documentation
-Consists of written or other visual information about an application system, how it works, and how to use it.
-Lists the item necessary to perform the task the user inquired about.
#https://bizfluent.com/facts-4962524-different-types-system-documentation.html
Implementation是SDLC里最长,最多东西要理解的,已经尽量不啰嗦了....很多再详细的东西还是需要大家自己去找,然后没有对training & support多加解释,因为我也不确定mpm要什么.....
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2.6 Maintenance Phase
Candidates should be able to:
(a) state the purpose of the maintenance phase;
(b) describe the activities in the maintenance phase: obtaining maintenance requests, transforming requests into changes, designing changes and implementing changes
Maintenance Phase
-Involves making changes to hardware, software, and documentation to support its operational effectiveness.
-To ensure that needs continue to be met and that the system continues to perform as per the specification mentioned in the first phase.
>维修,更新系统,有不要的功能也会被废除掉
-Activities:
- Obtaining maintenance requests
-Occur requirement changes from users and managers.
- Transforming requests into changes.
-Identify the requirement changes, cost.
- Designing changes
-Conduct system modifications.
-Execute changes design.
- Implementing changes
-Implement and test the changes.
-Ensure the changes are compatible to the existing system.
-Importance:
~Prevent system breakdown and failures.
~Bug fixing, search out the errors, and correct them.
~Enhance the capability, improve the features and functions.
~Remove outdated/unwanted functions
------------------------------------------------------------------------
SDLC是非常长,多东西背和理解的一个topic,SDLC出的问题也多,所以建议大家要好好理解每个phase(记得要做的活动,可能produce的report,参与人员等)
%3A+a+circuit+that+is+either+on+or+off.+Byte%3A+8+bits..jpg)