这个chapter会学到的topic:
1. Data, Information, Knowledge
2. ICT and Multimedia
3. CPU, Storage, Input, Output
4. System Software and Application Software
5. Communication Technology
6. Software Development Tools
7. Internet and WWW
8. Evolution of ICT Convergence
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Data
- simply any numbers, letters, or symbols that can be entered into a computer system.
- A raw material, need to be processed to turn into something useful.
- Exp: A, 20, DOG
- Data values don't have any meaning unless put into context (Setting or circumstance).
- Exp: 20 cm/ 20 minutes
- Data + context = information
//Data本身是没有意思的,单个data不能告诉一个有意义的数据/信息,但是给予data解释或者几个data合在一起,就可以提供有意义的数据、信息
Information
- Data that has been processed and is meaningful.
- Exp: 'Ali', 'Class A', '16' = Information of Ali
//被处理后的data组成有用的信息,可以提供信息给人去使用,比如decision-making
Knowledge
- Information and facts that can be learned
- The use and application of the information.
- Can be interpreted from the information.
//Information加起来组成一个可以用的,可以被理解,学习的知识。也可以说,information可以教会一个人技巧和经验。
总结:Data→Information→Knowledge
#有Notion的朋友可以到这个链接获取笔记:https://www.notion.so/Data-Information-Knowledge-9928aa53024d4da5b00f93fc55f9d472
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ICT
- Refers to all communication technologies such as the internet, wireless networks, cell phones, computers, software, and other media applications and services enabling users to access, retrieve, store, transmit, and manipulate information in a digital form.
- Refers to technologies that provide access to information through telecommunications. It is similar to Information Technology (IT), but focuses primarily on communication technologies. This includes the Internet, wireless networks, cell phones, and other communication mediums.
//简单来说,就是专注于沟通方式的技术/科技
Multimedia
- A combination of various types of media including sound/audio, image/graphics, animation, video, and text.
- The use of a computer to present and combine text, graphics, audio, and video with links and tools that let the user navigate, interact, create, and communicate.
//多媒体是集合声音,图片,动画,影片和文字的媒体
Text
- Most common multimedia element.
- Involves the use of text types, sizes, colours, and background colours
- Expresses the information the developer is trying to get across to their viewers.
- Format: *.txt, *.doc
//我说一下我怎样回答考题,假设我不记得text的definition,但是我知道text是multimedia的一种,就说,text is an element of multimedia that helps the user to express something to viewer. 类似于这样,我经常会用它们的功能去解释definition。
Image/Graphic
- Catches the viewers' attention much more quickly than just plain, old text.
- Help to illustrate ideas through still pictures.
- Common format: *.jpg, *.png
Audio
- Audio files are usually deployed using plug-in media players.
- A record of captured sound that can be played back.
- Sound or noise in a range the human ear is capable of hearing.
- Signal types: analog, digital
- Format: * .wav, *.midi
//后面会学到analog和digital sound是什么
Video
- Provides a powerful impact in a multimedia program.
- Starts with continuous event and breaks it up to frames.
- The moving pictures that accompanied by sound.
- Format: *.avi, *.mov, *.wmv, *.flv
Animation
- The process of making a static image to look as if it is moving.
- A method in which figures are manipulated to appear as moving pictures.
- A sequence of images that directly moves one after the other.
- Format: *.swf, *.gif
#详细的可以去http://smklunduictclass.blogspot.com/2012/07/4151-identify-multimedia-elements.html (推荐阅读,简单,容易明白)
#这部分刚开始会学的比较浅,因为后面会更深的去了解(包括它们的format和type,怎样形成,作用等,所以这里简单理解一下就好。也可以去找别的意思,不用跟着这里的。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- The portion of a computer that retrieves and executes instructions.
- The unit that performs most of the processing inside a computer.
- The brain of a computer that performs all types of data processing operations.
- Also called processor/ microprocessor/ central processor
//CPU是电脑的大脑,负责处理数据信息
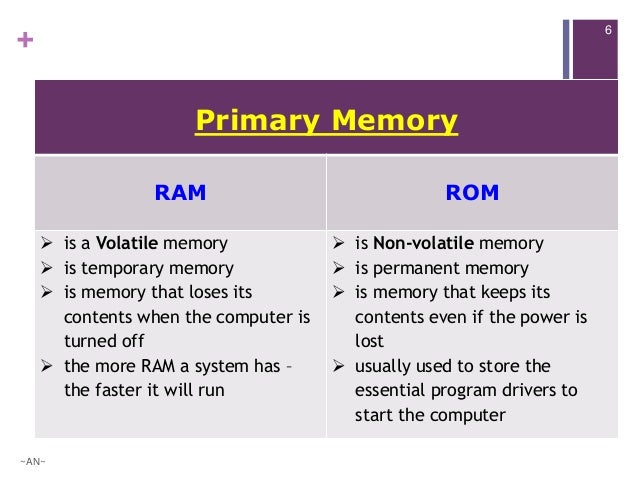
Storage
- Component of a computer that allows to store and access data on a long-term basis.
- A process through which digital data is saved within a data storage device by means of computing technology.
- A mechanism that enables a computer to retain data, either temporarily or permanently.
- Exp: flash drives, hard disks
- The main memory of the computer which can be directly accessed by the CPU.
- Volatile storage: requires a continuous supply of electricity to store/retain data.
- For temporarily storing data and handling application workloads.
- The external storage device which can be used to store data or information permanently.
- Non-Volatile Storage: a type of storage mechanism that retains digital data even if it’s powered off or isn’t supplied with electrical power.
- Is used for permanent data storage requiring I/O operations.
- Exp: Hard disk
//可以长久储存数据,而且即使没有通电/关机的情况下也会保留数据。外接电脑的#再仔细一点可以去看https://www.slideshare.net/andrewpp/ict-storage-devices
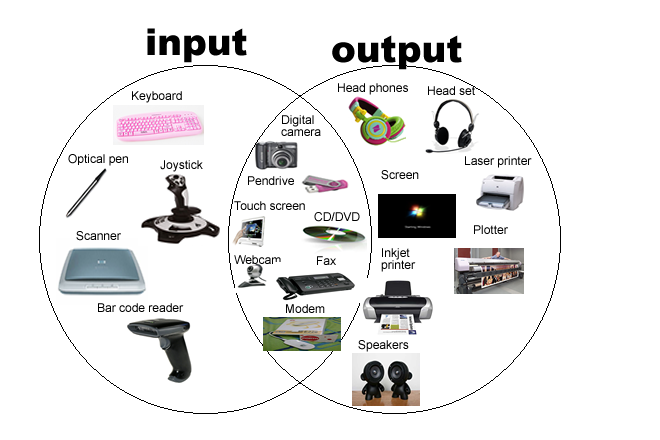
Input
- Data that a computer receives.
Input Device
- Device/hardware that connects to a computer that sends information into the computer.
- Hardware that is used to enter data and instructions by the user.
- Exp: keyboard, mouse, scanner, web camera, microphone
Output
- Data that a computer sends.
Output Device
- Device/hardware that connects to a computer that has information sent to it.
- Exp: monitor, printer, speaker
System Software
- A set of programs that control and manage the operations of computer hardware.
- It also helps application programs to execute correctly.
- Are designed to control the operation and extend the processing functionalities of a computer system.
- System software makes the operation of a computer more fast, effective, and secure.
- Exp: Operating system (OS), programming language, Communication software
//负责管理系统东西,例如memory and process management, security等
Types of System Software
- Operating systems(OS):
- Helps you with the effective utilization of all hardware and software components of a computer system.
-Exp: Windows, Mac OS, iOS, Ubuntu, Android
//帮助user使用操作电脑的hardware&software,记得OS=Windows就比较容易理解了 - Programming language translators:
- Transforms the instructions prepared by developers in a programming language into a form that can be interpreted or compiled and executed by a computer system.
-Exp: Visual Studio 2019
//把编程代码转换成电脑可以理解的语言(0和1), 电脑明白的语言只有0和1,叫binary code或者machine language。 - Communication Software:
- Communication software allows us to transfer data and programs from one computer system to another.
-Exp: web browser (Chrome, Microsoft Edge), e-mail (Gmail, Yahoo), instant messaging (WeChat, QQ) - Utility programs:
- A set of programs that help users in system maintenance tasks, and in performing tasks of routine nature.
-Exp: Anti Virus Program (McAfee), File Managers, Disk Cleaners
//帮助系统维护的工作的软件,常见如防毒软件,文件管理软件
Application Software
- A program that does real work for the user.
- It is mostly created to perform a specific task for a user.
- Acts as a mediator between the end-user and System Software.
- Written using a high-level language like C, Java, VB. Net
- It is user-specific and is designed to meet the requirements of the user.
//主要满足user的特殊要求,为了进行一些specific tasks
Types of Application Software
- Word-processing software:
- It makes use of a computer for creating, modifying, viewing, storing, retrieving, and printing documents.
-Exp: Microsoft Word - Spreadsheet software:
- Spreadsheet software is a numeric data-analysis tool that allows you to create a computerized ledger.
-Exp: Microsoft Excel - Database software:
- A database software is a collection of related data that is stored and retrieved according to user demand.
-Exp: Microsoft Access - Graphics software:
- It allows computer systems for creating, editing, drawing, graphs, etc.
-Exp: Microsoft PowerPoint - Education software:
- Education software allows a computer to be used as a learning and teaching tool.
-Exp: Google Classroom - Entertainment software:
- This type of app allows a computer to be used as an entertainment tool.
- Exp: Adobe Photoshop, video games
Communication Technology
- The transfer of messages (information) among people and/or machines through the use of technology.
- This processing of information can help people make decisions, solve problems, and control machines.
- Exp: Email, Short Message Services (SMS)
Computer Network
- A set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes.
- Uses common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other.
- A group of computers linked to each other that enables the computer to communicate with another computer and share their resources, data, and applications.
//一个以上的电脑连接其他电脑/设备所组成的网络
-
Type:
-
LAN (Local Area Network)
- A group of computers connected to each other in a small area such as building, office.
- Used for connecting two or more personal computers through a communication medium such as twisted pair, coaxial cable, etc.
- Less costly as it is built with inexpensive hardware such as hubs, network adapters, and ethernet cables.
- Data is transferred at an extremely faster rate.
- Provides higher security.
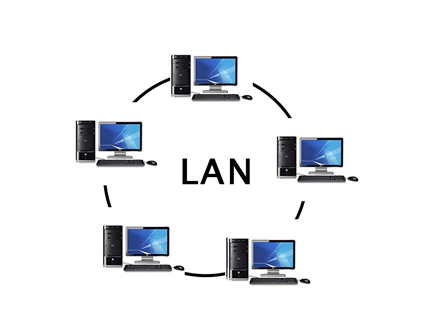
//LAN是比较小型,小范围的连接几个电脑的网络。比较便宜,可以用cable或者wireles来连接。
-
PAN (Personal Area Network)
- A network arranged within an individual person, typically within a range of 10 meters.
- For connecting the computer devices of personal use is known as Personal Area Network.
- Covers an area of 30 feet.
- Personal computer devices that are used to develop the personal area network are the laptop, mobile phones, media player, and play stations.
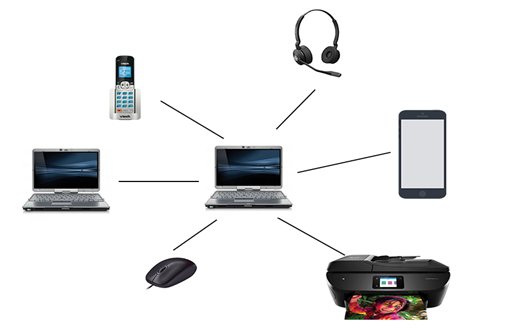
//个人电脑连接其他设备组成的网络
-
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- A network that covers a larger geographic area by interconnecting a different LAN to form a larger network.
- Government agencies use MAN to connect to the citizens and private industries.
- In MAN, various LANs are connected to each other through a telephone exchange line.
- Widely used protocols: RS-232, Frame Relay, ATM, ISDN, OC-3, ADSL, etc.
- Has a higher range than LAN.
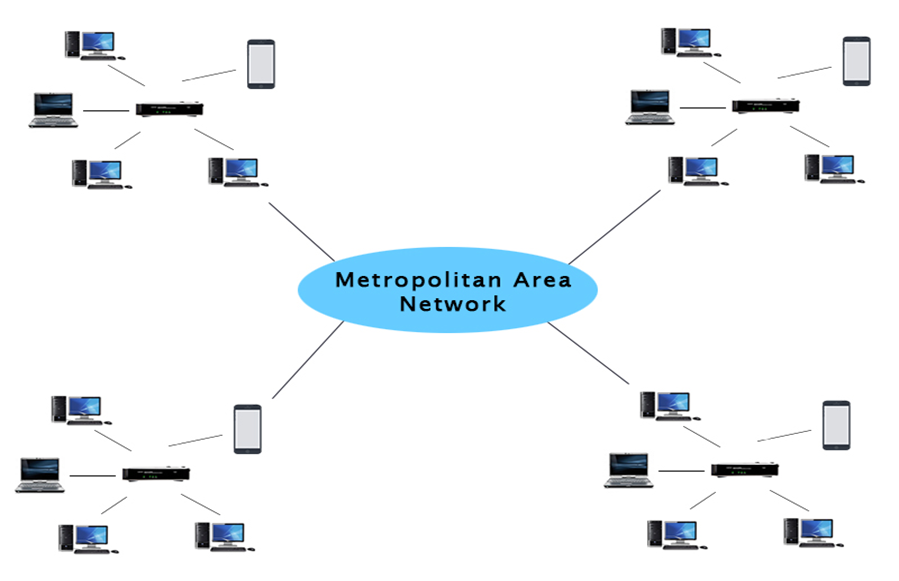
- Exp uses of MAN:
-Communication between the banks in a city.
-Airline Reservation.
-College within a city.
-Communication in the military.
-
WAN (Wide Area Network)
- A network that extends over a large geographical area such as states or countries.
- Bigger network than the LAN.
- Not limited to a single location, but it spans over a large geographical area through a telephone line, fiber optic cable, or satellite links.
- Exp: internet, mobile broadband
- Widely used in the field of Business, government, and education.
//例子:PAN是Ali个人电脑连接其他设备(printer,speaker等)。LAN是ALi和他几个同公司的同事电脑连接起来。MAN是Ali的母公司和其他同区的子公司连接起来的LAN。WAN是Ali在的地区和其他城市甚至不同国家的子公司连接起来的MAN。
-
- Network Topology:
- The arrangement with which computer systems or network devices are connected to each other.
- May define both physical and logical aspects of the network.
- Both logical and physical topologies could be the same or different in the same network.
- Types:
-
Bus Topology
- All the workstations, servers, and printers are joined to one cable - 'the bus'.
- At each end of the cable, a terminator is fitted to stop signals reflecting back down the bus.
//一条线,头和尾都有terminator。
- Advantages:
-easy to install
-cheap to install (does not require much cabling) - Disadvantages:
-If the main cable fails or gets damaged, the whole network will fail.
-As more workstations are connected, the performance of the network will become slower because of data collisions
-Every workstation on the network 'sees' all of the data on the network, which can be a security risk.
-
Star Topology
- Each device on the network has its own cable that connects to a switch or hub.
- Most popular way of setting up a LAN.
- May find a star network in a small network of five or six computers where speed is a priority.
//每个电脑or设备都是连接到hub/switch,所以其中一个设备坏了也不会影响其他设备,但如果hub/switch坏了,全部连接的设备电脑都不能用
- Advantages:
-very reliable (if one cable or device fails, then all the others will continue to work)
-high performing as no data collisions can occur - Disadvantages:
- Expensive to install as this type of network uses the most cable, and network cable is expensive.
-extra hardware is required (hubs or switches) which add to the cost
-If a hub or switch fails, all the devices connected to it will have no network connection.
-
Ring Topology
- Each device (eg workstation, server, printer) is connected in a ring so each one is connected to two other devices.
- Each data packet on the network travels in one direction.
- Each device receives each packet in turn until the destination device receives it.
//比如我要发文件给另一个电脑,假设我的是电脑A,我要传到电脑D,在ring topology里,我的文件会顺着A去D的方向传,结果就是电脑B和C也会收到这个文件直到传去电脑D才会停。

- Advantages:
-Can transfer data quickly (even if there are a large number of devices connected) as data only flows in one direction so there won't be any data collisions - Disadvantages:
-if the main cable fails or any device is faulty, then the whole network will fail (a serious problem in a company where communication is vital)
-
Point-to-Point
- Contains exactly two hosts such as computer, switches or routers, servers connected back to back using a single piece of cable.
- Often, the receiving end of one host is connected to sending end of the other and vice-versa.

- If the hosts are connected point-to-point logically, then may have multiple intermediate devices.
- But the end hosts are unaware of the underlying network and see each other as if they are connected directly.
Wired Communication Media
-
Wired Communication System
- Exists a physical media between the transmitter and the receiver using which the signal is transferred.
- Information is sent in form of electrical/optical signals.
- Used for short-distance communication (wire length increases, received signal quality decreases).
- Implementation is less complex than a wireless communication system.
-
Twisted-Pair Wire
- A copper wire that connects a personal computer at home or at work to the telephone line.
- Has two wires that are insulated to prevent wire crossing are twisted together.
- Least expensive communication media tool (made of copper)
- Frequency of carriers communication signals is relatively slow.

-
Coaxial Cable
- Armored cable with a sheathed plastic that contains two concentric conductors or wires.
- Used primarily for TV standard-definition connection to transfer television signal, and for computer network (internet connection) such as Ethernet to carry data.
- Because is much less susceptible to interference, it might carry much more data.
- Also, it is used to carry radio signal, video signal, and measurement signal.

Advantages:
- High Bandwidth
- Better noise Immunity
- Easy to install and expand
- Inexpensive
Disadvantages:
- Single cable failure can disrupt the entire network
-
Fiber-Optic Cable
- Consist of one or several thin fibers of glass or plastic of 50 to 125 micrometers of diameter.
- Signals are transmitted at the speed of light.
- Able to get a very fast transfer of information.

Advantages:
- Increased capacity and bandwidth
- Lightweight
- Less signal attenuation
- Immunity to electromagnetic interference
- Resistance to corrosive materials
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to install and maintain
- High cost
- Fragile
Wireless Communication Media
- Wireless Communication System
- Do not exist any physical media between the transmitter and the receiver.
- Information is transmitted using electromagnetic waves.
- Suitable for long-distance communication.
- Wireless Transmission Media
- Infrared (IR)
- Sends signals using infrared light waves.
- Used for very short distance communication.
- can not penetrate through obstacles. This prevents interference between systems.
- Used in TV remotes, wireless mouse, keyboard, printer, etc
- Microwaves
- Radio waves that provide a high-speed signal transmission.
- Involves sending signals from one microwave station to another.
- Can transmit data at rates up to 4,500 times faster than a dial-up modem.
- Majorly used for mobile phone communication and television distribution.
- Radio Waves
- a type of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum longer than infrared light.
- The sending and receiving antennas need not be aligned.
- AM and FM radios and cordless phones use Radiowaves for transmission.
- Communications satellite
- A space station that receives microwave signals from an earth-based station, amplifies (strengthens) the signals, and broadcasts the signals back over a wide area to any number of earth-based stations.
- These earth-based stations often are microwave stations.
- Other devices, such as smartphones and GPS receivers, also can function as earth-based stations.
- Broadcast radio
- Distributes radio signals through the air over long distances such as between cities, regions, and countries and short distances such as within an office or home.
- Exp: Bluetooth, UWB, Wi-Fi, and WiMAX communications technologies
- Cellular radio
- A form of broadcast radio that is used widely for mobile communications, specifically wireless modems and cell phones.
- A cell phone is a telephone device that uses high-frequency radio waves to transmit voice and digital data messages.
- Some mobile users connect their notebook computer or other mobile computer to a cell phone to access the Web, send and receive an e-mail, enter a chat room, or connect to an office or school network while away from a standard telephone line.
- Infrared (IR)
- Wireless Communication Device
- Mobiles
- GPS units
- Cordless telephones
- Radios
- A set of rules and regulations that allow two electronic devices to connect to exchange the data with one and another
- A system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any kind of variation of a physical quantity.
- The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics, and synchronization of communication and possible error recovery methods.
//Protocol是规矩(A set of rules and regulations), 允许两个以上的电子设备连接并互传不同类型的数据/信息( analog, digital, files, etc. )
- Function:
- to exchange messages from one computer system to another.
- cover error detection & correction, signaling, and authentication.
- explain the semantics, syntax & brings analog & digital communications together. - Types:
-
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP):
- Used for communicating over a network.
- A communications standard that enables application programs and computing devices to exchange messages over a network.
- It sends packets across the internet and ensures the successful delivery of data and messages over networks.
- TCP organizes data so that it can be transmitted between a server and a client
- Before it transmits data, TCP establishes a connection between a source and its destination, which it ensures remains live until communication begins. It then breaks large amounts of data into smaller packets, while ensuring data integrity is in place throughout the process.
//TCP是最常用的protocol之一。TCP的运作方式:在传送数据前,先建立目标和来源之间的连接。然后把大的数据包分成较小的数据包,在传送时确定数据完整性。 *Data Integrity:在传输、存储信息或数据的过程中,确保信息或数据不被未授权的篡改或在篡改后能够被迅速发现。
-
Internet Protocol (IP):
- Designed explicitly as addressing protocol.
- Method for sending data from one device to another across the internet
- Mostly used with TCP=Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP).
- The IP addresses in packets help in routing them through different nodes in a network until it reaches the destination system.
-
Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP)
- A combination of protocols (TCP and IP) that work together to ensure data is delivered to its intended destination within a network.
- The most popular protocol connecting the networks.
- IP obtains and defines the address (IP address) of the application or device the data must be sent to.
- TCP is then responsible for transporting and routing data through the network architecture and ensuring it gets delivered to the destination application or device that IP has defined.
//IP负责确定目的地地址,TCP负责通过网络来传输数据,并确定传输到正确的IP地址
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
- The transmission of voice and multimedia content over an internet connection.
- Allows users to make voice calls from a computer, smartphone, other mobile devices, etc.
- Exp Included features: video calls, audio calls, voicemail, e-mail, team chats.
- Uses an internet connection instead of a telephone company's wiring.
- A VoIP service will convert a user's voice from audio signals to digital data, then send that data through the internet.
- If another user is calling from a regular phone number, the signal is converted back to a telephone signal before it reaches that user.
-
USB Protocol (Universal Serial Bus)
- A serial communication of two-wire protocol.
- To communicate with the system peripherals.
- To send and receive the data serially to the host and peripheral devices.
- USB communication requires driver software that is based on the functionality of the system.
- USB devices can transfer data on the bus without any request on the host computer.
-
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP):
- HTTP is designed for transferring a hypertext among two or more systems.
- HTML tags are used for creating links. These links may be in any form like text or images.
- To load web pages using hypertext links.
- An application layer protocol designed to transfer information between networked devices and runs on top of other layers of the network protocol stack.
- Gives users a way to interact with web resources such as HTML files by transmitting hypertext messages between clients and servers
//Hypertext(超文本): text which contains links to other texts. 点击超文本就会跳转到另一个文档页面。
HTML: language for describing the structure of Web pages.
-
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS):
- A standard protocol to secure the communication among two computers one using the browser and other fetching data from web server.
- Used for transferring data between the client browser (request) and the web server (response) in the hypertext format, same in case of HTTP except that the transferring of data is done in an encrypted format.
- Thwart hackers from interpretation or modification of data throughout the transfer of packets.
- Exp: Banking websites
//跟http一样功能,只是更加安全
-
User Datagram Protocol (UDP):
- An alternative to TCP, which is used to establish low-latency connections between applications and decrease transmissions time.
- A substitute communication protocol to TCP, implemented primarily for creating loss-tolerating and low-latency linking between different applications.
- Does not provide error connection or packet sequencing nor does it signal a destination before it delivers data, which makes it less reliable but less expensive.
- A good option for time-sensitive situations, such as Domain Name System (DNS) lookup, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), and streaming media
-
Post office Protocol (POP):
- Designed for receiving incoming E-mails.
-
Simple mail transport Protocol (SMTP):
- Designed to send and distribute outgoing E-Mail.
-
File Transfer Protocol (FTP):
- Allows users to transfer files from one machine to another.
- Types of files may include program files, multimedia files, text files, and documents, etc.
-
Telnet:
- A set of rules designed for connecting one system with another.
- The connecting process here is termed as remote login.
- The system which requests for connection is the local computer, and the system which accepts the connection is the remote computer.
-
Gopher:
- A collection of rules implemented for searching, retrieving as well as displaying documents from isolated sites.
- Also works on the client/server principle.
-
Software Development Tools
- A computer program that software developers use to create, debug, maintain, or otherwise support other programs and applications.
- Tools that help programmers to create software.
Programming Languages
- Give instructions to a computer in a language that the computer understands.
- Languages that help programmers to give instructions to the computer to perform specific tasks.
- Exp: C, C++, Java, Phyton
- Types:
-Functional Programming Language
-Procedural Programming Language
-Logic Programming Language
-Object-oriented Programming Language
#顺便一说Sem 2会学C programming
Mark-up Languages
- A computer language that uses tags to define elements within a document.
- It is human-readable, meaning markup files contain standard words, rather than typical programming syntax.
- Usually either specify how something should be displayed or what something means
- Exp: HTML, XML

Scripting Languages
- A programming language that is interpreted.
- It is translated into machine code when the code is run, rather than beforehand.
- Often used for short scripts over full computer programs.
- Use interpreter to compile a code line by line.
- Exp: JavaScript, Python,Ruby
//SL=PL, 但PL≠SL。最大区别是compiler,PL是直接整个code一起compile,SL是line by line。 *Compile:把code转换成电脑明白的语言
#更多对比看:https://www.codingninjas.com/blog/2018/12/08/difference-between-a-programming-language-and-a-scripting-language/
Authoring Tools
- A program designed for use by a non-computer expert to create e-learning products
- A programming language used to create tutorials, computer-based training courseware, websites, CD-ROMs, and other interactive computer programs.
- An authoring system does not require programming knowledge to operate.
- It allows the placement of graphics, text, and other multimedia elements into an e-learning program.
- It functions like word-processing software.
- Exp: HTML, XML

Internet
- A vast network that connects computers all over the world.
- A global network of networks.
- The biggest worldwide communication network of computers.
- The global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices.
- Through the Internet, people can share information and communicate from anywhere with an Internet connection.
- Support human communication via social media, electronic mail (e-mail), “chat rooms,” newsgroups, and audio and video transmission
- Support access to digital information by many applications, including the World Wide Web.
//Interenet是computer network的一种。用来连接设备(全球性)
World Wide Web (WWW)
- Collection of information which is accessed via the Internet.
- Combination of all resources and users on the Internet that are using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
- A collection of websites or web pages stored in web servers and connected to local computers through the internet.
- An information system where documents and other web resources are identified by Uniform Resource Locators (URLs, such as https://example.com/), which may be interlinked by hyperlinks, and are accessible over the Internet.
- The internet consists of supporting infrastructure and other technologies. In contrast, the Web is a communications model that, through HTTP, enables the exchange of information over the internet.
- Also called 3W or Web
//3W≠Internet,3W更多像一个工具,Internet像渠道。
//百度解释:3W基于hypertext和HTTP的、全球性的、动态交互的、跨平台的分布式图形信息系统。是建立在Internet上的一种网络服务,为浏览者在Internet上查找和浏览信息提供了图形化的、易于访问的直观界面,其中的文档及hyperlink将Internet上的信息节点组织成一个互为关联的网状结构。
- Convergence: Refers to two or more things coming together, joining together or evolving into one.
- Occurred when digital media, telecommunications, and computer technologies (ICTs) merged to produce ICT.
- The ability of different computing devices, services, or networks to provide different services over a common platform.
- Exp: Camera+Phone+Software= communication
- Benefits: //合理就可以
-Expanded access
-Greater competition
-Increase investment
-Lower cost
-Improve user experience
//最常见的例子就是手机,一部手机集合了各种科技,例如拍照功能,录音,音乐,通讯等。很多时候用手机当例子就可以。
Media Convergence
- Refers to the merging of previously distinct media technologies and platforms through digitization and computer networking.
- The merging of different types of mass media such as Traditional Media, Print Media, Broadcast Media, New Media, and the Internet as well as portable and highly interactive technologies through digital media platforms
- Exp:
- Smartphones (converging camera, music, the internet, books, and all other media together)
- Online Radio (converging radio with the Internet)
- E-books (converging paperbacks with the digital technology)
- News Websites and Apps
- Refers to the trend or phenomenon where two or more independent technologies integrate and form a new outcome.
- The ability for different technological systems to evolve toward performing similar tasks.
- A term that describes bringing previously unrelated technologies together, often in a single device.
- Exp: Smartphone, tablet, laptop, desktop computer
Communication Convergence
- Integration of voice, data, and video networks systems and signaling infrastructure in a single unified networking system.
- How:
-IP as common transport platform
-SIP as common signaling protocol -IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS): an emerging architecture of converged fixed and mobile networks - Involves a combination of:
-Electronic media
-Telecommunication media
-Broadcast media
#Syllabus要的是evolution of ICT convergence in information(content), computer and communication.







资料准备的好棒,可以跟着做笔记,期待你的更新!!
回复删除